In Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011 and Microsoft Dynamics CRM Online, you use field-level security to restrict access to high business impact fields to specific users and teams. For example, you use this to enable only certain users to read or update the credit score for a customer. For this release, field security can be applied to custom fields only.
The following steps describe how to restrict access to a field:
- Create a field security profile.
- Associate users or teams with the profile.
- Add specific field permissions, such as Create, Update or Read to the profile.
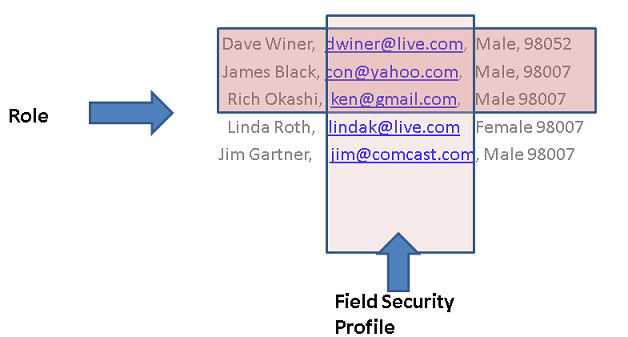
The following diagram shows the interaction between role-based security, record-based security, and field-based security.
 |
| Field level security administration |
Role-based security lets you see a specific entity type, record-based security lets you see individual records, and field-level security lets you see specific fields.
Which Security Roles Allow You to See Secured Fields?
The System Administrator field security profile gives full access to all secured fields in Microsoft Dynamics CRM. By default, all users who have the System Administrator security role have this profile. This profile is system managed and cannot be updated or deleted.
How Do Secured Fields Behave for Retrieve and RetrieveMultiple?
When you call the Retrieve or RetrieveMultiple methods or messages, Microsoft Dynamics CRM evaluates if the caller and the impersonated user have access to each retrieved record (this is the regular security process) and each secured field. The call does not throw an exception if the criteria contain secured fields for which the caller does not have access. Instead, null values are returned for secured fields if they are part of the output column set.
The following describes more about the retrieve multiple behaviors for secured fields.
When a Secured Attribute is in the Column Set
If the caller (or impersonated user) does not have read access to the secured fields that are included in a column set, the value returns as null. You cannot tell the difference between a returned null value caused by no data or caused by insufficient access.
When a Secured Attribute is in the Filter Condition
If the caller (or impersonated user) does not have access to the secured fields that are included in the filter criteria, the field value is substituted with null during the evaluation of the filter.
In the following table, the caller has access to attributes that are in plain text. The caller does not have access to attributes that are in Bold or Italic format.
Record: 1
Name: A
Description: AAA
CanbeContacted: True
Record: 2
Name: B
Description: BBB
CanbeContacted: False
Record: 3
Name: C
Description: CCC
CanbeContacted: True
Record: 4
Name: D
Description: DDD
CanbeContacted: Null
Record: 5
Name: E
Description: EEE
CanbeContacted: Null
When the filter is CanbeContacted == True, only record one is returned.
When the filter is IsNULL (CanbeContacted), records 3 and 4 are returned. Since record 3 is hidden from the user, it is treated as null during condition evaluation and will be evaluated as True for ISNull.
When Aggregating on Secured Attributes
Secured values are substituted with a null value, so normal SQL aggregation behavior applies.
When Grouping on Secured Attributes
If the caller (or impersonated user) does not have access to the attribute used for grouping, the value is treated as null and the results are grouped together with all null values.
In the following example, the caller has access to attributes that are in plain text. Bold indicates no access to attributes. Italics indicate a record for which the caller does not have read access.
Name: A
Description: AAA
Number of orders: 1
State: WA
Name: B
Description: BBB
Number of orders: 4
State: WA
Name: C
Description: CCC
Number of orders: 4
State: CA
Name: D
Description: DDD
Number of orders: 3
State: MA
Name: E
Description: EEE
Number of orders: 0
State: CA
Name: F
Description: FFF
Number of orders: 0
State: WA
Name: G
Description: GGG
Number of orders: 2
State: CA
Select State, Total(orders) Group by (STATE) results in the following:
When Ordering on Secured Attributes
If the caller (or impersonated user) does not have access to secured fields that are included in an order by condition, the values will be treated as if they are null.
In the following example, the caller has access to attributes that are in plain text. Bold indicates no access to attributes, and Italics indicate a record for which the caller does not have read access.
Name: A
Description: AAA
CanbeContacted: True
Name: B
Description: BBB
CanbeContacted: False
Name: C
Description: CCC
CanbeContacted: True
Name: D
Description: DDD
CanbeContacted: Null
Name: E
Description: EEE
CanbeContacted: Null
Name: F
Description: FFF
CanbeContacted: True
Name: G
Description: Null
CanbeContacted: True
Select Name order by Description ascending results in the following:
{G,E,C},A, B, D, will be returned.
How Do Secured Fields Behave for Create or Update?
A programmer may build a client that uses Create and Update methods that interact with secured fields. When you call the Create or Update method, passing data for secured fields and the caller does not have sufficient permissions, an exception is thrown.
How Do Secured Fields Behave When Records are Shared?
A user with access to a secured field in a record can choose to share it with another user or team. The user can only give the access that they have on the record. For example, to share the record and grant Update privileges, the user must have update privileges.
You can share a secured field on a particular record with Read and/or Update with a security principal (user or team). The user or team members with whom the record was shared now have that type of secured field access only on the shared secured fields on only that particular record, even if the user or team member to whom it was shared does not have a field security profile that gives them access.
How Do Secured Fields Behave for Filtered Views?
An administrator secures a number of fields for access in the application and wants the fields not to be available in reports. This allows for maintaining the same set of reports for all users. Filtered views will not return data for the secured fields if the calling user does not have authorization for the fields. When no field security is applied for any of the view’s attributes, the filtered views return complete data.
How Do Secured Fields Behave for Offline Synchronization?
If you are using Microsoft Dynamics CRM for Microsoft Office Outlook with Offline Access, only the secured field values to which you have access replicate into the offline database. If you do not have access to the data, it is not saved offline.
My above blog is based on Microsoft's Official information.
I
hope this blog about 'Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011 - How Field Security Can Be Used to Control Access to Field Values' was informative.
Please feel free to leave your
comments.